

TRADE BLOCS FREE
We introduce a new trade bloc variable that relies on the. Countries establish trading blocs because they believe free trade benefits their consumers by providing higher quality at lower cost. Within PTAs, however, there is a strong, inverse relationship between commerce and conflict. This study investigates the economic geography of international trade during the period 19502005. Global commerce is rapidly organizing around regional trading blocs in North America, Western Europe, Pacific Asia, and elsewhere-with potentially. Trading blocs : alternative approaches to analyzing preferential trade agreements. Based on an analysis of the period since World War II, we find that trade flows have relatively little effect on the likelihood of disputes between states that do not participate in the same PTA. The recent proliferation of free trade areas and customs unions in the. Moreover, we maintain that heightened commerce is more likely to inhibit conflict between states that belong to the same preferential grouping than between states that do not. Trading Blocs builds on a growing body of research into political economy and domestic politics, challenging the tendency to explain international trade. These sectors urge their governments to take. We argue that parties to the same PTA are less prone to disputes than other states and that hostilities between PTA members are less likely to occur as trade flows rise between them. It is argued that trading blocs have negative economic effects on economic sectors in non-members states. Before going further, Trade Block, trading bloc, trade bloc will be used interchangeably in this article.

These blocs are made up of a group of contiguous countries that decide to have common trading policies for the rest of the world in terms of tariffs and market access but have preferential treatment for one another. Definition of Trade blocs: A trade bloc is an association of countries that work together to provide special deals for trading.These regional trade blocs promote trade between countries within the bloc. 1 responsible for trade polity of members and negotiates agreements 2 engages with others to negotiate trade agreements 3 grant mutually beneficial access to markets. In this article we present some initial quantitative results pertaining to the influence on military disputes of preferential trading arrangements (PTAs), a broad class of commercial institutions that includes free trade areas, common markets, and customs unions. TRADING BLOCS An evolving trend in international economic activity is the formation of multinational trading blocs. worlds largest trading bloc, worlds 2nd largest economy.
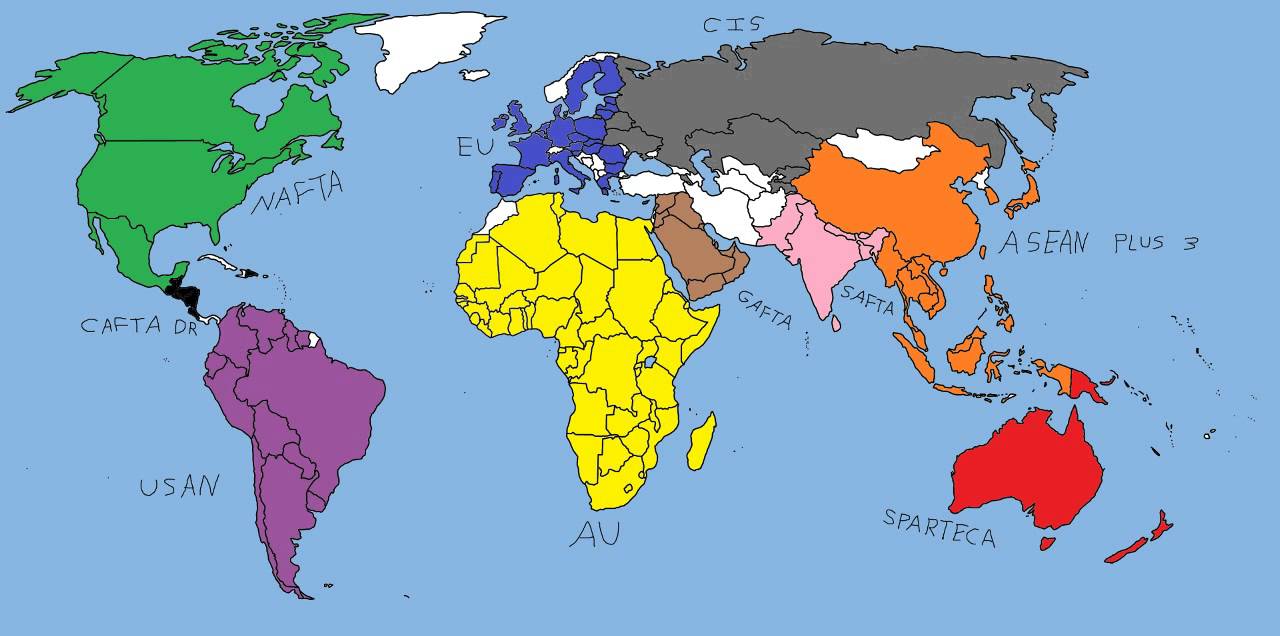
Existing empirical studies of this topic have focused on the effects of trade flows on conflict, but they have largely ignored the institutional context in which trade is conducted. The United States has agreements in force with 20 countries.
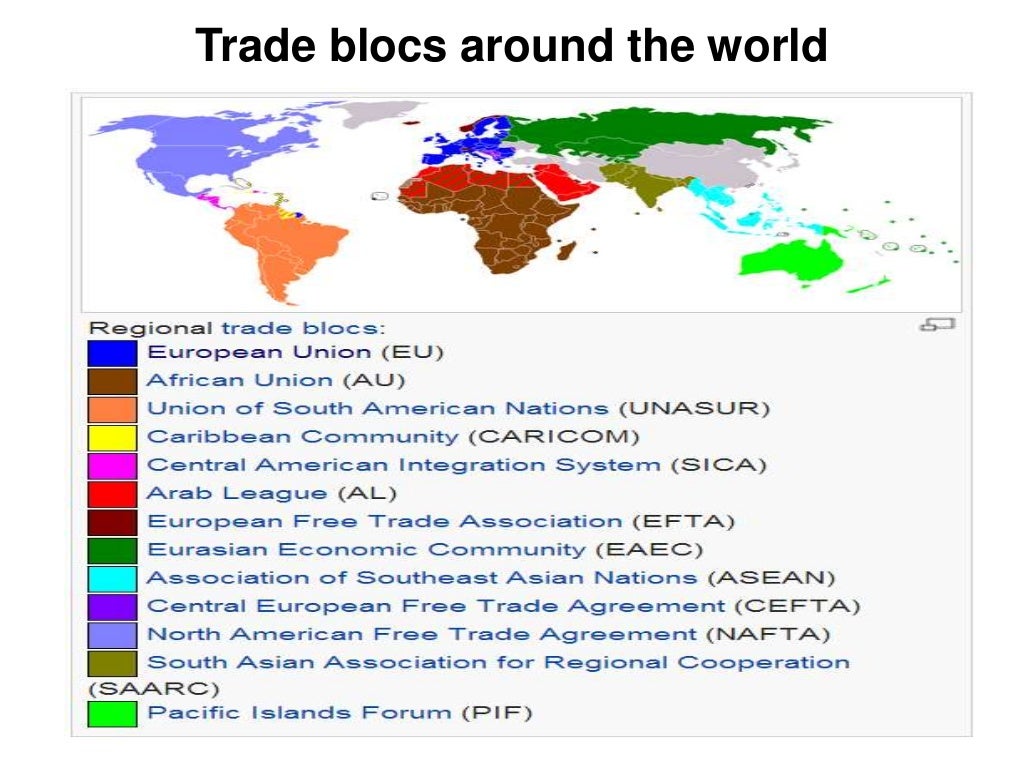
!(././././././././././var/folders/34/zq18d8kx7kbgby0j06p_j6t40000gn/T/TemporaryItems/NSIRD_screencaptureui_EM2XPo/Screenshot at 17.01.16.The relationship between foreign trade and political conflict has been a persistent source of controversy among scholars of international relations. Trade agreements are one of the best ways to open up foreign markets to U.S. More speculatively, we argue that the trade wars of the present day may serve a similar purpose as those in the 1930s, that is, the intensification of China- and US-centric trade blocs. We argue that the trade wars mainly served to intensify pre-existing efforts towards the formation of trade blocs which dated from at least 1920. What precisely were the causes and consequences of the trade wars in the 1930s? Were there perhaps deeper forces at work in reorienting global trade prior to the outbreak of World War II? And what lessons may this particular historical episode provide for the present day? To answer these questions, we distinguish between long-run secular trends in the period from 1920 to 1939 related to the formation of trade blocs (in particular, the British Commonwealth) and short-run disruptions associated with the trade wars of the 1930s (in particular, large and widespread declines in bilateral trade, the narrowing of trade imbalances, and sharp drops in average traded distances). Discussion paper DP13716 Trade Blocs and Trade Wars during the Interwar Period The criticism of trade blocs is the difficulty smaller, less developed nations have in joining them.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
